Table of Contents

Filmmaking is the art of capturing what the artist wants to show. It is the act of creating art with a camera in accordance with one’s wishes. The most important thing in film-making is having control over what your camera records. If you change basic settings, you will have greater control over your shots. In this article. We will be learning how to manipulate your camera settings to achieve the best Photographic or Cinematic experience.
There are several factors that must be considered to produce a good quality image. The first factor is the type of lens. The lens you use can affect the look and style of your shot. Films such as Requiem for a Dream, American Beauty, and Leon. The Professionals all use different lenses to create very different looks and styles on their images.
You should consider the following aspects: which camera do you want to shoot on. And what kind of budget do you have? If you want to shoot on a digital video camera. Avoid shooting in DV DV 25 or DV 50 mode because they look poor. When played back on computer monitors or home DVD players.
If you want to shoot on a digital camera or a video camera. You should shoot as much as possible in the 24 fps (frames per second) standard for film. In 24 fps progressive, the individual frames are scanned progressively – from the top to the bottom across the screen. Creating a more film-like image.
Many digital video cameras shoot in 30p, which is not true frame by frame. But instead, three frames are recorded and displayed every one frame cycle. On a DVD if you select ‘frame advance’ it will look jerky compared with real film material shot at 24p. If your budget permits, use 35mm film.
READ ALSO: How to remove freckles in Photoshop
WHAT IS CAMERA?
A camera refers to a device that records pictures of an object. It has a light-sensitive plate attached to the object that enables the object to be seen. And a lens that acts as a magnifier.
HOW CAMERA OPERATES: Manipulating your Camera Settings.
The Camera consists of two parts: Lens, which focuses light from the subject onto the film or image sensor; Film or Image Sensor. Which converts light rays into electrical signals which correspond to the image. As seen by the naked eye. In other words, it is an optical instrument used for taking images.
WHAT TO CHECK WHEN PURCHASING A DSLR CAMERA?
Lens
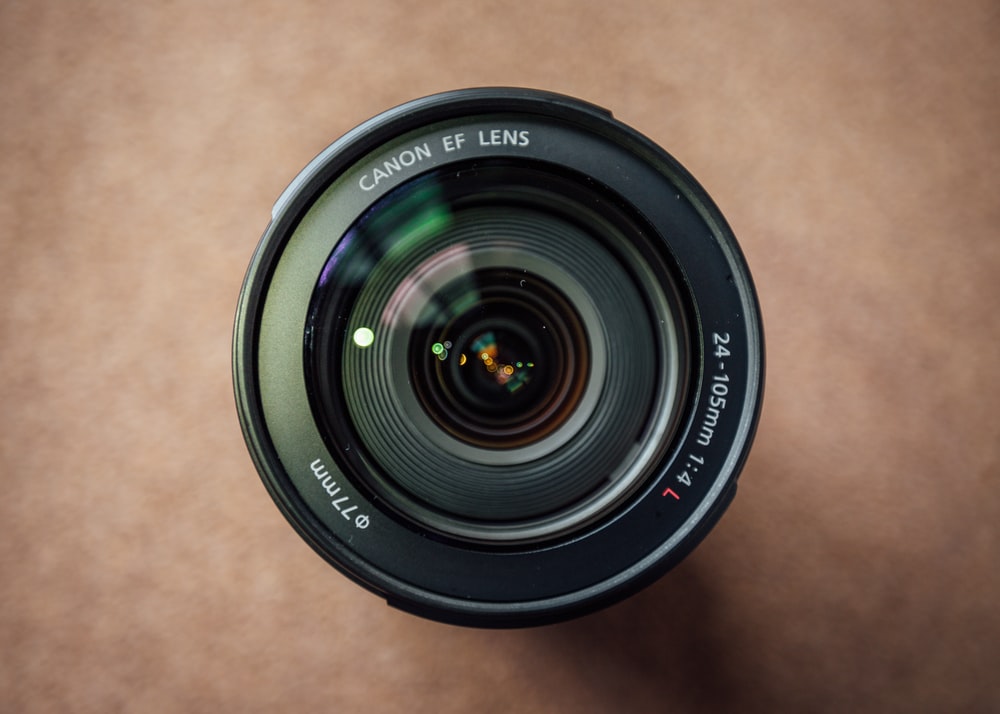

The lens is an important part of the camera because it focuses light rays onto the film or image sensor. The lens will gather rays from many different directions and converge them to produce an image of the object. It also serves as a magnifier, projecting the image in the lens onto the film or sensor.
This is why in low-light situations, you should always use a tripod. Or stay in one place to avoid blur in your shots. To find out what kind of focal length you want for your shot, refer to what is the focal length (approx 200).
Focus
The camera needs to focus in order to form an image on the film or sensor. The process in which the lens focuses is called focusing. There are two ways of focusing: automatic and manual focus. When using automatic focus, the lens produces a sharp image without you having to do much adjustment. With manual focus, however, you need to adjust the position of the lens manually. If it does not produce a sharp image when shooting your shot.
Shutter

The shutter is a mechanical device that controls the exposure time during which light rays reach the film or sensor. It can be controlled in different ways. But it usually consists of two curtains, one sliding in front of the other to block. Or open the camera lens to expose the film or sensor. The two basic modes are: automatic and manual, which you should use according to your needs. When shooting in automatic mode, set your camera to A (aperture priority), S (shutter priority), or TV (time value). The aperture determines how much light enters the camera. Without specifying how long it would take for that ray of light to travel across the lens.
Focus Screen
A focus screen is a small screen that you can see through the camera’s viewfinder. To assist you in focusing the camera. It is also known as a viewfinder, eyepiece, or finder. You may choose to use your eyes for focusing or may use the screen. You can adjust the focus with this screen by adjusting your position or distance from it.
Film
The film is not only an image sensor but also allows light rays to travel through it. By absorbing light rays during the development process. Three film types are available: motion picture film (shot on 35mm), regular (shot on regular 35mm film), and super (shot on super 16mm).
A Camera uses photographic film to capture images. The exposed film is chemically processed before being printed onto photographic paper. And then be made ready for viewing or printing purposes.
In both film and digital video cameras, the ‘shutter speed’ is the length of time the shutter remains open to allow light into the camera. The higher the shutter speed, the brighter a scene will appear. Lowering a shutter speed increases the amount of light recorded. But this has an effect on how much motion blur there will be in a shot. You should then decide how fast you want your shot to move. For example, you could slow down if it’s a very emotional moment or speed up for more action.
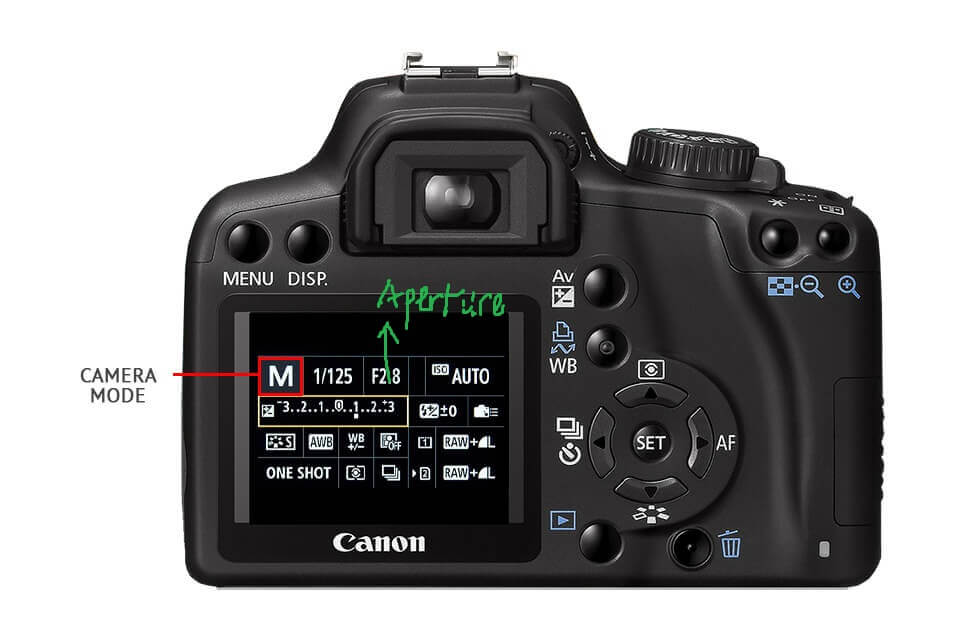

The ‘aperture’ is an opening inside your lens that adjusts to let in different amounts of light. Depending on which setting you have chosen.
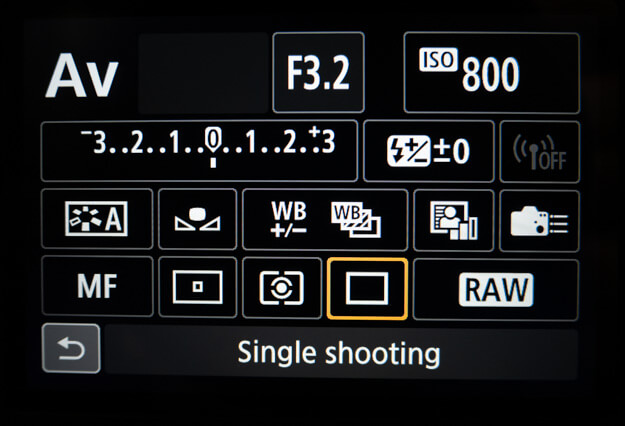
Some of the most important settings you can set for your camera are shutter speed, aperture, ISO, contrast, sharpness, and white balance. These are the lens settings that control depth of field and depth of focus. Temperature plays a key role in photography as well with several settings. All these settings are accessible in different menus via your camera or on your digital video camera. There is no universal setting for every shot. And the settings vary from camera to camera which is why you need to experiment with them. Until you find what works best for you.
Portable or Digital?
Portable cameras are sold at a higher price point because of the additional features they include. The best cameras are usually equipped with advanced features. Such as optical viewfinders, interchangeable lenses, large dynamic range sensors, high-resolution LCDs. And many more which make it easier for photographers to do their job right. Usually, the higher the prices are, the better the camera is.
Digital cameras consist of a digital image sensor and image processing system (which may include an image sensor depending on the specific type of camera). Usually, they have video capability, and can be made portable or not.
They often include features such as still picture recording, movie recording, storage in memory cards and internal storage, and battery power. Digital cameras were originally designed for consumers who wanted to use a smaller and less expensive device. Better than camcorders and SLR-style cameras to take pictures of their family or vacation. While digital cameras have become more consumer-friendly. They still aren’t as easily portable as a basic point-and-shoot camera.
The file format used for digital cameras depends on the type of camera, modes of modes available, and usage. The first step should be to determine if you’re going to be viewing your pictures on a TV set, a computer screen, a printer, or transferred to an image card. Or a USB flash storage device. For personal use pictures were taken on the desktop are best stored in JPEG format.
If you plan to email your pictures consider using an attachment. That will fit in storage capacity instead of offering low-quality images as attachments. Many digital cameras today use the RAW file format. It’s kind of like a digital negative where you have more options for editing. Most professional photographers consider it to be the highest quality image. But you have to use software that can handle it to get the benefit of its quality.
Olympus LS-10C – Sound on/off switch
Spare battery pack(optional)
3MP, 1/4″ CCD image sensor, DSP sound enhancement system, 12x optical zoom lens, 2.5 inch TFT LCD display screen, 5x digital optical zoom.
HOW TO MANIPULATE DSLR CAMERA SETTINGS
Aperture:
The aperture is the opening in the lens that allows light to enter your camera and expose your picture. The size of this hole can be reduced (or made smaller). By turning the wheel on the front of your lens, it will say “F” or “F-stop” after this wheel. The larger the number, the smaller the hole; if you want a large depth of field (the area where everything is in focus), such as an entire landscape picture. You’ll want to set your F-stop to a lower number so more light can enter.
Shutter Speed:
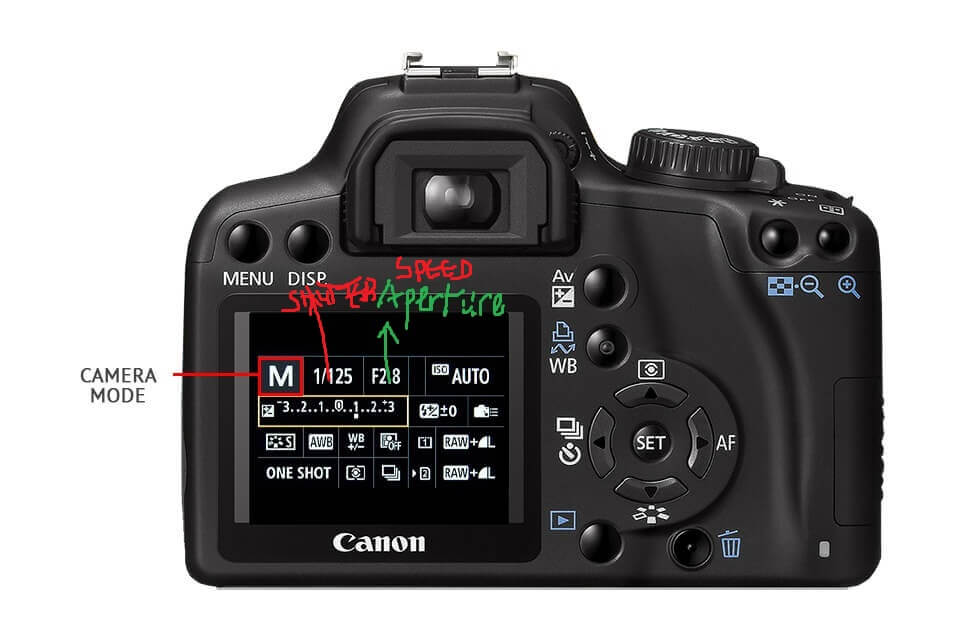

The shutter speed is how much time it takes for a photon to hit your sensor or film and expose your picture. The shutter speed is measured in seconds. But you will see it written as 1/60, 1/100, 1/250, etc. If you are taking a picture of people skiing and the light conditions are low. Or if it is foggy outside you may need to stop down your aperture for a wider opening so more light can enter. If you are using the camera indoors where there is plenty of light. Then keep your aperture smaller so that the shutter speed can be higher.
ISO:
This stands for International Organization for Standardization also known as ASA (American Standards Association) in North America and DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung) in Germany. The ISO is a method to properly expose your film. The higher the number, the less light that is required. If your camera offers a lot of different settings this number will be listed on different menus. Or on the outside of your camera. If you are shooting outdoors in bright sunlight. It will be very important to keep your ISO as low as possible. To make sure pictures are not overexposed.
Exposure Compensation:
This button allows you to “over or underexpose” one side of an image by adding or subtracting exposure time from the other side of the image. A negative exposure compensation adjustment will darken the picture while a positive adjustment will brighten it. This is especially important for high-contrast scenes that have a very bright light object. Such as a face on a mountain, and a very dark background. You will need to adjust your exposure compensation button. Until the subject of your picture is sharp and clear with no blown-out highlights or shadows on the other side of the image.
White Balance:
White balancing is an adjustment to correct colors produced. By artificial light sources such as sodium lamps, tungsten lamps, fluorescent lamps, and electronic flash. Often this is done automatically using auto white balance systems in digital cameras. But older film cameras required manual adjustment of the white balance settings. The user will usually adjust this setting to obtain better color representation.
Macro Mode:
Macro mode is an adjustment to change the point of focus for greater close-up ability. This mode allows the user to make smaller adjustments to their depth of field because it can focus very close to its subject. The depth of field is what makes a photograph sharp or blurry. A macro image should be sharp from front to back, not just near the front or far away from the lens.
Some cameras are capable of capturing images in raw format, or uncompressed image data recorded by special sensors that can capture photos with greater range exposure compared to conventional camera sensors. Raw images are generally larger in size because they contain more picture data, and as a result require greater storage space. For the best results from your raw images, you will need specific image-editing software to edit them. There is a great number of software available for editing RAW images, including free software such as digiKam and dark table or paid-for software such as Adobe Photoshop or Corel AfterShot Pro.
While consumer digital cameras usually allow the user to choose the compression rates for storing images on a memory card, professional film cameras often depend on a fixed number of quality settings that determine the balance between image quality and quantization (the process of reducing the size of an image file).
In the case of a digital camera, compression can be achieved in a number of ways:
Each method has its advantages and disadvantages. A high-quality compression method can encode an image with lower numbers of bits, or bytes, but it will do worse on heavily textured areas. A low-quality compression will use many more bits to encode an image, but this will lead to a better resolution on textured areas at the expense of reduced resolution for large uniform areas.
Some methods of storing video data are also applied to still images, such as MPEG1 (Motion Pictures Experts Group) and JPEG2000 (ISO/IEC 15444-1).
There are several general types of film. Black & white film is made with either silver halide grains or light-metabolizing chemicals and then processed to produce a negative image of each frame. Color negative film is made by combining black and white images in some way. Color print film is usually the same size as an 8×10 print and gives a color image when processed to dye it black and white. It can also be used to give your negatives an additional layer of color for special effects.
These are not the only uses for photographic film, nor are they the only types that are popularly available, but these are some typical formats. In addition, there are two main types of film: film for photography and motion picture film. Motion picture film is usually larger in size but uses the same emulsion as 35mm stills.
In addition to the general variety of emulsion used, there are a number of chemical processes that can be applied to it after it has been developed. The most common ones are:
35mm and medium format cameras allow for interchangeable lenses and other accessories such as flashguns and filters that give the user greater control over their images. This is one of the reasons that they are often more expensive cameras. Cameras are also more complex these days especially with the ability of digital cameras to record HD video.
A number of camera manufacturers have started to offer point-and-shoot digital cameras that provide 3×3, 4×4 or 8×8 pixel photos for around US$50. They are typically used by parents with young children who do not have much shooting experience and have had little practice at taking photos on their own.
A camera phone is a mobile phone with an integrated camera. To make them easy to use, they generally do not provide manual control of exposure and focus. They typically produce lower quality images than standalone digital cameras, because of their small sensors and lenses and low-quality cameras that reduce processing power requirements.
Digital cameras typically allow the user to preview the image on the display before taking it. This is called “Live Preview”. While some cameras can preview images in real-time, such as in smartphone cameras, this is usually limited to a few seconds or minutes; most try to provide a delay of several seconds.
Digital cameras with video recording capability make capturing and editing videos easier than regular digital still cameras. Some digital still and compact cameras (DSC and CCD) can take video and shoot it in 4:3 or 16:9 formats. Video is then recorded onto an internal memory that is usually much larger than the amount of data that can be stored in a typical digital still camera.
Most digital still cameras (DSCs) include a display screen on which you can review and edit your pictures. In most cases, this screen will be an LCD screen but some have been known to have a TFT Organic light-emitting diode display or OLED display. Most DSCs have a built-in flash but some models can use an external flash unit.
Some of them can also be used as a webcam which is useful if you want to take pictures of someone else while they’re using the camera you are using. Most DSCs also has other features including the ability to take photos in burst mode, pre-programmed scene modes, or other special modes that need special software or other devices.
Some digital still cameras have the ability to shoot movies at different frame rates, including movie mode which allows users to shoot video at fixed frame rates. For example, the Canon EOS 1D Mark IV is capable of shooting up to 60 fps. Depending on the camera, movie mode can be used to take quick videos or for slow-motion playback. Some movie modes are designed to create videos with special effects.
Digital cameras that use image sensor technology rather than the film can provide higher image quality than their film equivalents because they do not require processing in the camera. They also have improved dynamic range and improved low light sensitivity than their film counterparts. However, they are more sensitive to light and require stronger batteries than standard cameras with an analog sensor which reduces their battery life by 25% compared to film cameras of equivalent size.

3 thoughts on “How to Manipulate your Camera settings”