Table of Contents
In photography, the goal of focusing is to obtain a sharp image with a correctly sized depth-of-field. This is a tricky thing for many beginners to do. But it all comes down to understanding what you’re going for in your shot. Once you have that in mind, focusing can be easier and smoother. A lot of photographers use magnification aids such as binoculars. Or telescopes in order to get their focus right before they snap the picture. However, Focusing techniques in DSLR for improving photography skills, if you are working from home with your DSLR camera without these tools around for some reason, this article will teach you how to obtain adequate focus on your photos without relying on aids or any other tools.
READ ALSO: QUALITY BACKDROPS FOR PHOTOGRAPHY
REASON FOR SHOOTING
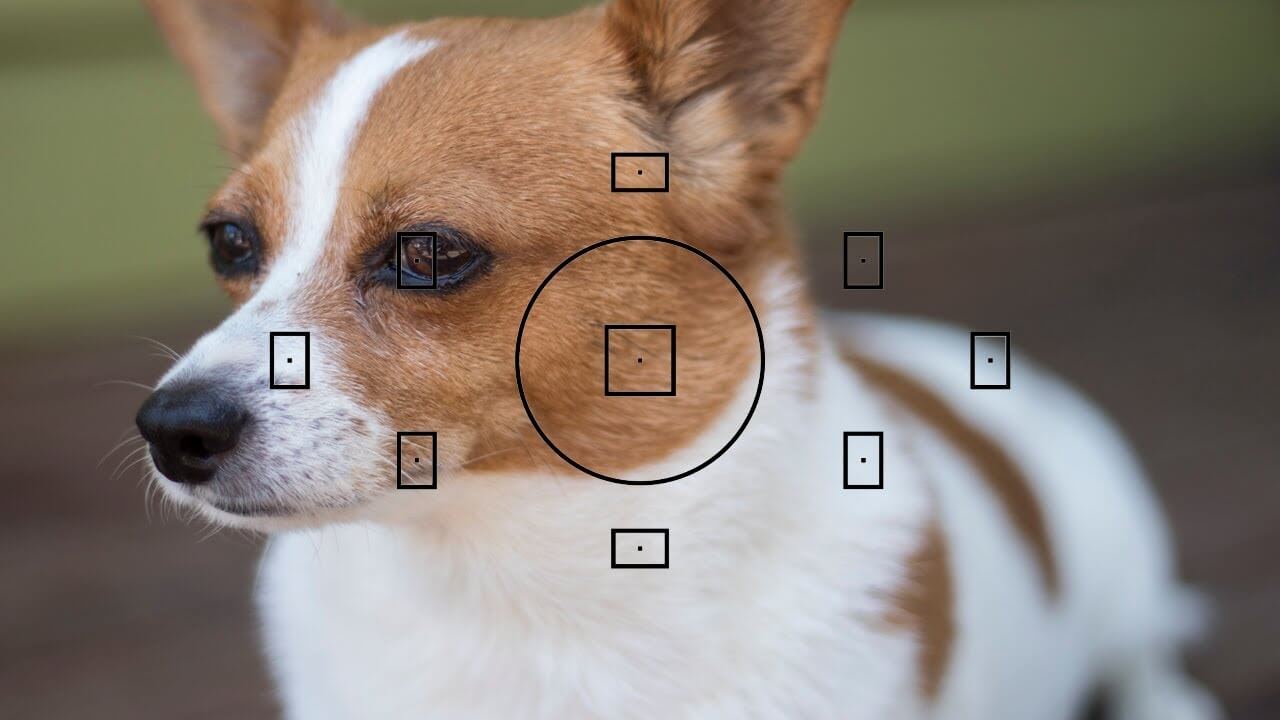
The first step in learning the focusing techniques is to consider what you are taking a shot for. For example, if you’re shooting someone on-stage acting. You may be trying to get their face in focus with the background out of focus. This way, the audience will only see their face and the emotion they portray on stage. Focusing techniques are desired by many photographers for things like portraits or artwork. Where there is little or no background visible. On the other hand, if you were taking a picture of a raccoon raiding your trash can. It would be best to get its face in focus while keeping your trash can blurry so that it’s unclear what exactly it’s rummaging through.
FOCUSING

Another thing to consider is the area you’re focusing on or using a focusing technique. For example, if you were taking a picture of a bird on your lawn. It would be best to focus on the bird and blur its surroundings out. However, if you were taking a picture of a person in front of your house. It’d be best to keep their face and everything around it in focus. This way, the viewer will be able to see everything clearly alongside the main subject focused on.
CHECK OUT ALSO: HDR merge
Once your focus is set upon an area, you must then clarify how much depth-of-field that area contains. This means that you should take a shot. Or two just to see how much of the photo contains your area of focus. You want to ensure that the depth-of-field you are getting is correct. So just taking a few shots to get this right will help you tremendously in the long run.

The ultimate thing to understand before focusing is how your camera’s aperture controls depth-of-field. If you don’t calculate aperture correctly, your photos could come out blurred or “out of focus”. The aperture affects what numbers appear on your camera’s lens. All it really means is the opening where light enters your camera lens. To get put onto film or digital sensor. This opening has several numbers on it, but the ones you are concerned about are the f-number. You can either set your aperture to f-2.8, f-5.6, f-8, or whatever your camera lets you choose. The lower your number gets, the more depth-of-field you have in the photo.
FOCUSING ON MOVING OBJECTS
The last part of focusing is being able to focus on moving objects. For example, if you’re at a baseball game and want to get a picture of a player running to base. And sliding in before he’s tagged out by an opposing player. It’s impossible to focus in this situation. You either need to use some kind of focusing aid or take the picture while the player is still. This way, you can get your object in focus while the background is left blurry.
Using binoculars is one of the easiest ways to focus on something that’s moving. For example, if I were trying to get a shot of my cat running across my floor. I would just put binoculars on her and then snap away. I could even use this same technique with people. However, it becomes harder when you want to get shots of people working out at the gym. Or doing other physically demanding tasks where they are moving fast enough. That you need more than binoculars to get their picture in focus.
The truth is that if you can master focusing your DSLR camera, you’ll be able to take better shots. Having everything in focus can make or break a photographer’s career; It’s one of the biggest aspects of photography and should be taken seriously. By everyone wanting to get out there and make their name as a photographer. Just remember: depth-of-field is what controls your photo’s sharpness. The lower your f-number, the more detail will be rendered in your image.
FOCUSING FEATURES IN DSLR CAMERAS
Focusing is generally done in two ways when using a digital single-lens reflex (DSLR) camera. One method is autofocus, which allows the camera to do all of the focusing and tracking. Auto-focusing works slightly differently on different cameras, but usually. It will detect a moving subject and then attempt to keep that subject in focus throughout the exposure. The second type of focusing is manual focusing. Manual focusing lets you move your camera’s focus ring (or sometimes another control mechanism such as rotating wheels) manually. To get the focus you want.
CONTINUOUS F/AUTO FOCUS
One type of auto-focusing system is called “continuous f/autofocus”. This system works similarly to autofocus on a well-designed autofocus camera. But does not change focus unless you tell it to. It tracks moving objects by reading the distance between the object and the lens. The only way to stop tracking is to raise your camera’s shutter speed enough. That the object is no longer within range of focus. This type of focusing can cause problems if you are not careful with your depth-of-field. As the camera will remain focused on an area that is too small or too large. Neither of which can be corrected with depth-of-field compensation. Thus, continuous f/autofocus systems are best used for subjects where tracking isn’t important (e.g., photographing landscapes).
SINGLE F/AUTO FOCUS
Another type of auto-focusing is called “single f/autofocus”. This system works as a single-lens reflex camera, as it takes a picture the moment the shutter is pressed. The camera then auto-focuses before taking the picture. This can cause problems when you are using too slow of a shutter speed. Since you have no time to re-adjust your focusing distance before taking the picture. Continuous f/autofocus systems are more desirable for people that need to track moving objects. Because they allow you to release the shutter at any time. Whereas single f/autofocus systems will not let you take a photo unless everything in your picture is in focus.
Some cameras allow you to manually focus, while others only focus automatically. When manually setting your focus, you must be aware of certain settings that are present on most modern cameras. These include “focus distance settings” and “depth-of-field settings”.
RELATED ARTICLE: Ecommerce solutions for professional Photographers
FOCUS DISTANCE
Focus distance settings are simply the distances at which your camera will focus. Depth-of-field settings, on the other hand, control how much of the image you will be able to have in focus. Even after focusing on a particular subject. These two options can be used together so that both are near. And far objects are in focus at the same time. The distance at which your camera will focus is determined. By how far away from the lens you place your camera’s focusing ring. The depth-of-field settings are the controls that allow the user to control how much of an image will be in focus. Either by adjusting the aperture or by adjusting your camera’s shutter speed.
Some cameras feature “image stabilization” (also known as “lens stabilization”) or VR (or VRII) technologies. That compensates for changes in the focal distance when taking a picture. This allows one to take long exposures without worrying about blurring. VR technology uses special sensors to sense motion; otherwise, VR systems are not viable for single-lens reflex cameras due to their large size and weight.
FOCUS STACKING
Focus stacking is usually used in macro photography to capture an image where there is a focus at several different distances. These photos are achieved by taking several images of the same subject with different focal ranges. Then combine them into one image using the software. For example, an image of a mouse might be in focus in one part of the picture. But blurred at other parts because it was not in focus in the camera. This type of photography can be done manually. Or with specialized hardware like rails to make sure that all parts of the photo are at the correct distance.
Because digital cameras use solid-state electronics to capture an electronic signal rather than film. They don’t require cleaning as conventional cameras do. However, there are a few things that you should do to keep your digital camera functioning properly.
One challenge that many photographers have with digital cameras is cleaning. Over time, dirt and dust can build up on the lens and the sensor. Which leads to a blurry picture as well as decreased light sensitivity from the sensor. You can usually clean off this dirt using a blower or compressed air. This step is usually necessary whenever you first start using your camera. Or before every vacation where there might be lots of sand and salt around.
A manual can tell you things like: “Do not use aerosol sprays. Because they contain solvents which will damage the electronic parts of the camera”. However, the use of aerosols is not prohibited. The best thing to do is to read your camera’s manual on the safe use of sprays. And using compressed air to clean.
You can also blot off any dust or dirt by using a lint-free cloth, microfiber cloth, or paper towel. Shop around for quality blowers and compressed air if you’re determined not to use aerosols. Use caution when using aerosols; some may be fogging agents which can cause long-term damage to the electronics in your camera (particularly if it is an all-weather sealed model). Also note that, like with any electronic equipment, some people get static shocks from contact with static electricity. If you have a static shock, touch the metal part of the camera before touching yourself.
Static cling can also cause problems with digital cameras. You can avoid static in your camera by using a static-sensitive cloth to clean your camera. If there is a static storm, use a lint-free cloth to wipe off any dust from the sensor before taking the picture.

1 thought on “Focusing techniques in DSLR for improving photography skills”